Importing and exporting data
This section describes the available tools to import and export data.
Overview
Spine Database Editor supports importing and exporting data in three different formats: SQLite, JSON, and Excel. The SQLite import/export uses the Spine Database format. The JSON and Excel import/export use a specific format described in Format specifications.
Importing
To import a file, select File –> Import from the hamburger menu. The Import file dialog will pop up. Select the file type (SQLite, JSON, or Excel), enter the path of the file to import, and accept the dialog.
Tip
You can undo import operations using Edit -> Undo.
Exporting
Mass export
To export items in mass, select File –> Export from the hamburger menu. The Export items dialog will pop up:
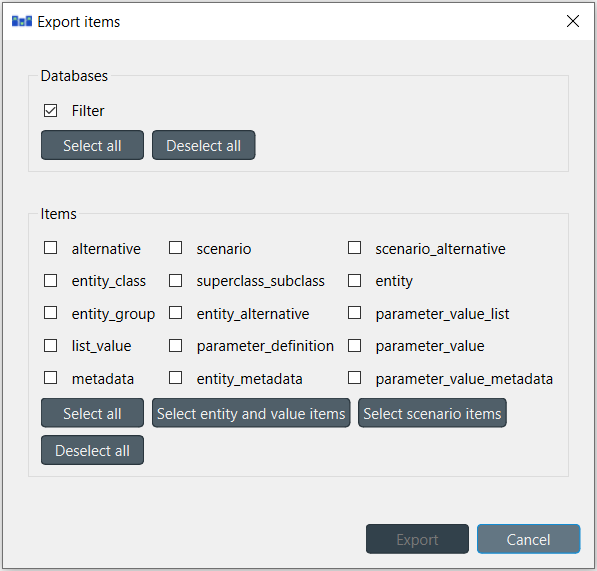
Select the databases you want to export under Databases, and the type of items under Items, then press Ok. The Export file dialog will pop up now. Select the file type (SQLite, JSON, or Excel), enter the path of the file to export, and accept the dialog.
Selective export
To export a specific subset of items, select the corresponding items in the Entity Tree, right click on the selection to bring the context menu, and select Export.
The Export file dialog will pop up. Select the file type (SQLite, JSON, or Excel), enter the path of the file to export, and accept the dialog.
Session export
To export only uncommitted changes made in the current session, select File –> Export session from the hamburger menu.
The Export file dialog will pop up. Select the file type (SQLite, JSON, or Excel), enter the path of the file to export, and accept the dialog.
Note
Export operations include all uncommitted changes.
Accessing/using exported files
Whenever you successfully export a file, a button with the file name is created in the Exports bar at the bottom of the form. Pressing that button will open the JSON or Excel file with the default program that your system associates with that filetype. Exports of SQLite file type will be opened in a new tab of the Spine Database Editor. To open the folder containing the export, click on the arrow next to the file name and select Open containing folder from the popup menu.
Format specifications
Tip
To create a template file with the JSON or Excel format you can simply export an existing Spine database into one of those formats.
Excel format
Note
Excel exports are not comprehensive. Even though every type of item is selectable in the exporting selection, sheets will be generated only for some of the selections. Things like metadata and parameter value lists don’t currently have export support with excel. The JSON export on the other hand is comprehensive and will export every detail about the database.
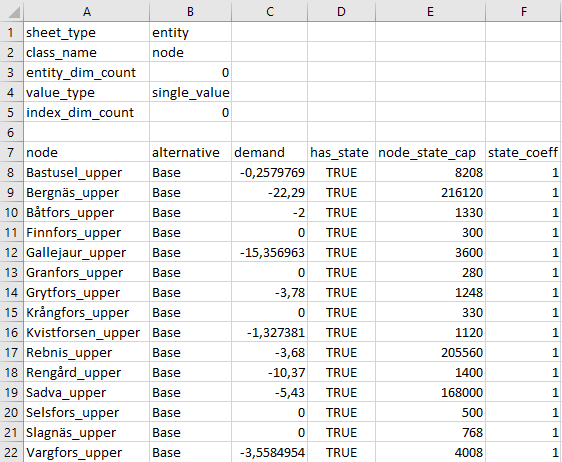
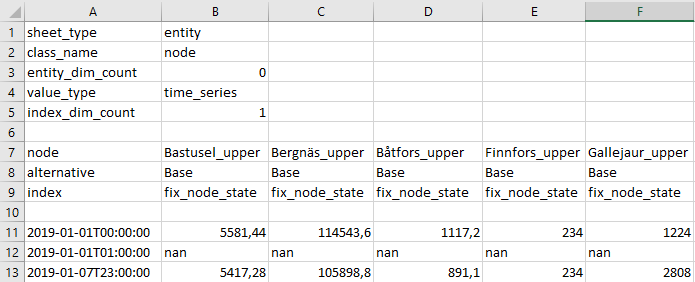
When parameter values are exported, the generated Excel will have every entity class on its own sheet. If the entity has indexed values (time-series, map etc.) as well as single values (floats, strings etc.) the entity will have more than one sheet, one containing the single values and others that unpack the indexed values:
scalar parameter data:
indexed parameter data:
JSON format
The JSON export is complete since it contains all of the data from the database.
The JSON format consists of a single JSON object with the following OPTIONAL keys:
entity_classes: the value of this key
MUSTbe a JSON array, representing a list of entity classes. Each element in this arrayMUSTbe itself a JSON array andMUSThave three elements:The first element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the entity class name.The second element
MUSTbe a JSON array, indicating the member entity classes. Each element in this arrayMUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the entity class name. In case of 0-D entity class, the array is empty.The third element
MUSTbe either a JSON string, indicating the entity class description, or null.The fourth element
MUSTbe either a JSON integer, indicating the entity class icon code, or null.The fourth element
MUSTbe a JSON boolean, indicating the state of active by default.
superclass_subclasses: the value of this key
MUSTbe a JSON array, representing a list of superclasses. Each element in this arrayMUSTbe itself a JSON array andMUSThave two elements:The first element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the superclass name.The second element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the subclass name.
entities: the value of this key
MUSTbe a JSON array, representing a list of entities. Each element in this arrayMUSTbe itself a JSON array andMUSThave three elements:The first element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the entity class name.The second element
MUSTbe a JSON array, if the entity is N-dimensional. In this case each element in the arrayMUSTbe a JSON string itself, each being an element of the entity. If the entity class is 0-D, this elementMUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the entity name.The third element
MUSTbe either a JSON string, indicating the entity description, or null.
Entity alternatives: the value of this key
MUSTbe a JSON array, representing a list of entity alternatives. Each element in this arrayMUSTbe itself a JSON array andMUSThave four elements:The first element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the entity class name.The second element
MUSTbe either a JSON array or a JSON string. In the case of a N-dimensional entity the arrayMUSTitself contain JSON strings representing the element name list of the entity. If the entity is 0-D, a JSON string of the name of the entity is enough, but also a JSON array of one element is supported.
entity_groups: the value of this key
MUSTbe a JSON array, representing a list of entity groups. Each element in this arrayMUSTbe itself a JSON array andMUSThave three elements:The first element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the entity class.The second element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the entity group name.The third element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the member entity’s name.
parameter_value_lists: the value of this key
MUSTbe a JSON array, representing a list of parameter value lists. Each element in this arrayMUSTbe itself a JSON array andMUSThave two elements:The first element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the parameter value list name.The second element
MUSTbe either a JSON object, string, number, or null, indicating the value.
parameter_definitions: the value of this key
MUSTbe a JSON array, representing a list of parameter definitions. Each element in this arrayMUSTbe itself a JSON array andMUSThave five elements:The first element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the entity class name.The second element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the parameter name.The third element
MUSTbe either a JSON object, string, number, or null, indicating the parameter default value.The fourth element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the associated parameter value list, or null.The fifth element
MUSTbe either a JSON string, indicating the parameter description, or null.
parameter_values: the value of this key
MUSTbe a JSON array, representing a list of entity parameter values. Each element in this arrayMUSTbe itself a JSON array andMUSThave four elements:The first element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the entity class name.The second element
MUSTbe a JSON array, if the entity is N-dimensional. In this case each element in the arrayMUSTbe a JSON string itself, each being an element of the entity. If the entity class is 0-D, this elementMUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the entity name.The third element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the parameter name.The fourth element
MUSTbe either a JSON object, string, number, or null, indicating the parameter value.
There is one
OPTIONALelement:The fifth element
MUSTeither be a JSON string indicating the alternative, or null. If this element is not present, an alternative named Base will be created if it doesn’t exist and the values will be set in that alternative.
alternatives: the value of this key
MUSTbe a JSON array, representing a list of alternatives. Each element in this arrayMUSTbe itself a JSON array andMUSThave two elements:The first element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the alternative nameThe second element
MUSTbe either a JSON string, indicating the alternative description, or null.
scenarios: the value of this key
MUSTbe a JSON array, representing a list of alternatives. Each element in this arrayMUSTbe itself a JSON array andMUSThave two elements:The first element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the scenario name.The second element
MUSTbe a JSON boolean, indicating the scenario alternative active state.The third element
MUSTbe either a JSON string, indicating the scenario description, or null.
scenario alternatives: the value of this key
MUSTbe a JSON array, representing a list of alternatives. Each element in this arrayMUSTbe itself a JSON array andMUSThave three elements:The first element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the scenario name.The second element
MUSTbe a JSON string, indicating the alternative name aowfiuhwaofiajw.
Example:
{
"entity_classes": [
["connection",[],"A transfer of commodities between nodes. E.g. electricity line,gas pipeline...",280378317271233,true],
["node",[],"A universal aggregator of commodify flows over units and connections,with storage capabilities.",280740554077951,true],
["unit",[],"A conversion of one/many comodities between nodes.",281470681805429,true],
["unit__from_node",["unit","node"],"Defines the `nodes` the `unit` can take input from,and holds most `unit_flow` variable specific parameters.",281470681805657,true],
["unit__to_node",["unit","node"],"Defines the `nodes` the `unit` can output to,and holds most `unit_flow` variable specific parameters.",281470681805658,true],
["connection__node__node",["connection","node","node"],"Holds parameters spanning multiple `connection_flow` variables to and from multiple `nodes`.",null,true]
],
"entities": [
["connection","Bastusel_to_Grytfors_disch",null],
["node","Bastusel_lower",null],
["node","Bastusel_upper",null],
["node","Grytfors_upper",null],
["unit","Bastusel_pwr_plant",null],
["unit__from_node",["Bastusel_pwr_plant","Bastusel_upper"],null],
["unit__to_node",["Bastusel_pwr_plant","Bastusel_lower"],null],
["connection__node__node",["Bastusel_to_Grytfors_disch","Grytfors_upper","Bastusel_lower"],null]
],
"parameter_value_lists": [
["balance_type_list","balance_type_group"],
["balance_type_list","balance_type_node"],
["balance_type_list","balance_type_none"]
],
"parameter_definitions": [
["connection","connection_availability_factor",1,null,"Availability of the `connection`,acting as a multiplier on its `connection_capacity`. Typically between 0-1."],
["connection__node__node","connection_flow_delay",{"type": "duration","data": "0h"},null,"Delays the `connection_flows` associated with the latter `node` in respect to the `connection_flows` associated with the first `node`."],
["node","balance_type","balance_type_node","balance_type_list","A selector for how the `:nodal_balance` constraint should be handled."],
["node","demand",0,null,"Demand for the `commodity` of a `node`. Energy gains can be represented using negative `demand`."],
["node","fix_node_state",null,null,"Fixes the corresponding `node_state` variable to the provided value. Can be used for e.g. fixing boundary conditions."],
["node","has_state",null,null,"A boolean flag for whether a `node` has a `node_state` variable."],
["unit__from_node","unit_capacity",null,null,"Maximum `unit_flow` capacity of a single 'sub_unit' of the `unit`."],
["unit__to_node","unit_capacity",null,null,"Maximum `unit_flow` capacity of a single 'sub_unit' of the `unit`."]
],
"parameter_values": [
["connection__node__node",["Bastusel_to_Grytfors_disch","Grytfors_upper","Bastusel_lower"],"connection_flow_delay",{"type": "duration","data": "1h"},"Base"],
["node","Bastusel_upper","demand",-0.2579768519,"Base"],
["node","Bastusel_upper","fix_node_state",{"type": "time_series","data": {"2019-01-01T00:00:00": 5581.44,"2019-01-01T01:00:00": -1,"2019-01-07T23:00:00": 5417.28}},"Base"],
["node","Bastusel_upper","has_state",null,"Base"],
["unit__from_node",["Bastusel_pwr_plant","Bastusel_upper"],"unit_capacity",170,"Base"]
],
"alternatives": [
["Base","Base alternative"]
]
}